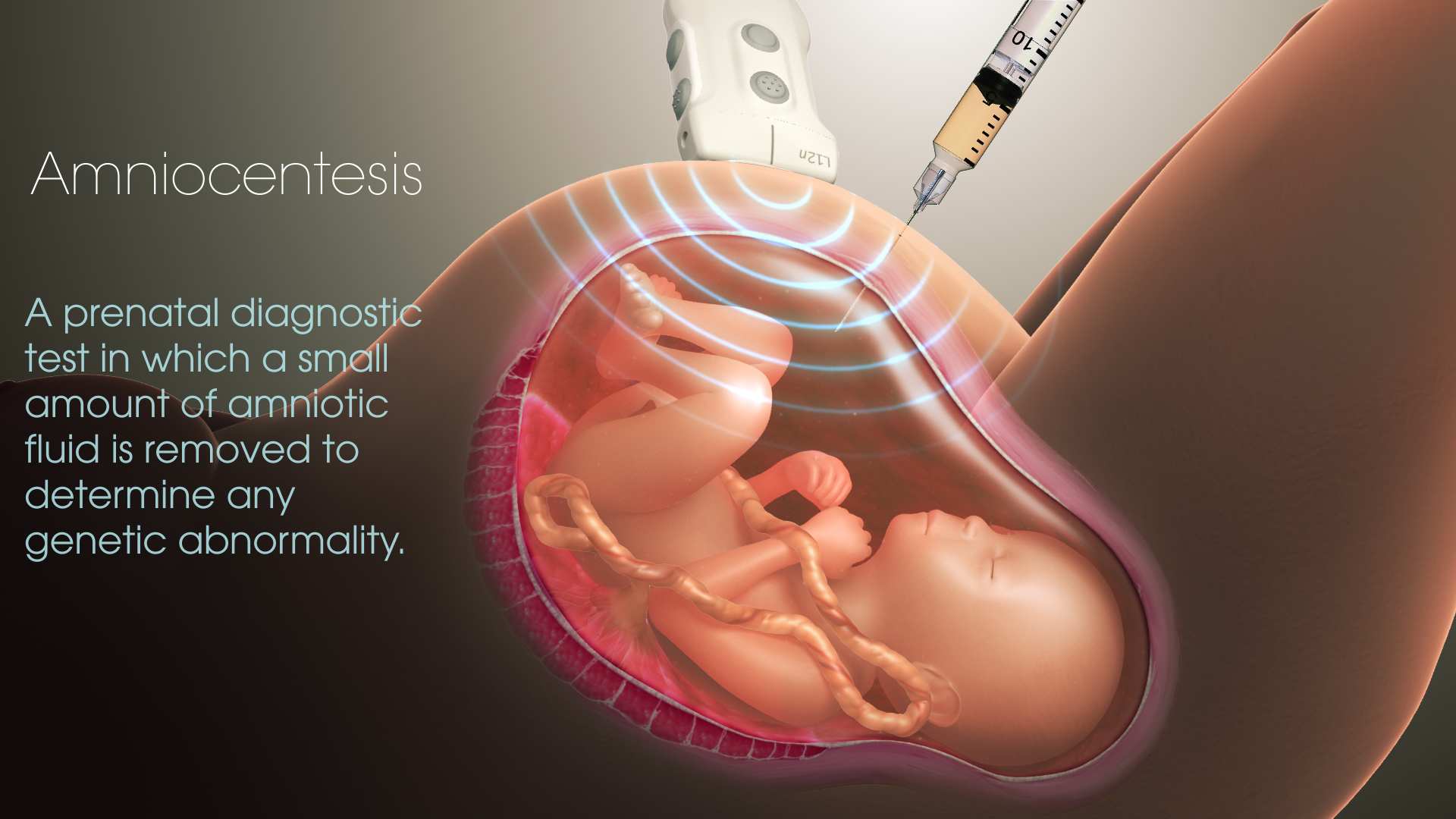
What Are The Risks Of Having An Amniocentesis – Amniocentesis is a prenatal test given to women between 15 and 20 weeks of pregnancy to determine if the baby has a genetic or chromosomal abnormality, such as Down syndrome. It requires the doctor to use a needle and ultrasound to take a small sample of amniotic fluid.
Amniocentesis is a prenatal test done to determine if the baby has certain genetic disorders or chromosomal disorders, such as Down syndrome. It is usually done between 15 and 20 weeks of pregnancy, but it can be done at any time after that.
What Are The Risks Of Having An Amniocentesis

Just like Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS), which is done in the first trimester, amniocentesis produces a karyotype, a picture of your baby’s chromosomes, so your nurse can see for sure if there are any abnormalities.
Amniocentesis: Risks, Alternatives, Purpose, & More
The test requires a healthcare professional to use a needle and ultrasound to take a small sample of amniotic fluid, the fluid that surrounds your baby in the womb.
Although all women should be given an amniocentesis, women who choose to have this test are always at greater risk of genetic and chromosomal problems, because the test is invasive and has a small risk of miscarriage.
Amniocentesis cannot detect birth defects, such as heart defects or cleft lip or palate. Many structural defects can be seen in the ultrasound of the second trimester, which is done normally for every woman.
What factors put me at higher risk of having a baby with a genetic abnormality or problem?
Getting Pregnant After 35: Here Is What You Need To Know
You had a first trimester test that shows your baby has a high risk of Down syndrome or another chromosomal problem. First-trimester screening includes a nuchal translucency scan (NT scan) and a cell-free fetal DNA test (noninvasive prenatal testing, or NIPT).
You and your partner are carriers of a genetic disease such as cystic fibrosis or sickle cell disease.
You have been pregnant with a baby with the abnormal gene and may be at high risk of it happening again.

You or your partner have a chromosomal abnormality or genetic disorder or family history that increases your child’s risk of genetic disorders.
Amniocentesis: Risks, Results, Accuracy, And More
Anyone can have a baby with a chromosomal abnormality, but the risk increases with the mother’s age. For example, your chance of carrying a child with Down syndrome increases from 1 in 1,200 at age 25 to 1 in 100 at age 40.
The risk of miscarriage caused by amniocentesis is small. Since a certain percentage of women end up with a miscarriage in the second trimester anyway, it is impossible to know for sure if the miscarriage after amniocentesis is caused by the procedure.
Estimates vary, but according to the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), the miscarriage rate is as low as 1 in 769. Some studies show a lower risk.
Other risks include passing an infection (such as HIV or hepatitis) from you to your baby and leaking amniotic fluid. Leakage of amniotic fluid is usually a small amount (absorbed by your body) and stops on its own within a week.
Quad Screen: Uses, Side Effects, Procedure, Results
Oh yeah. In fact, most testing centers require you to meet with a genetic counselor to discuss the risks and benefits of various prenatal testing methods and testing methods before an invasive procedure such as amniocentesis or CVS. The counselor will take your family history and ask you questions about your pregnancy.
Using your answers, the counselor can give you an idea of your risk of having a child with chromosomal problems or a certain genetic disease. Then you can decide if you want a screening, go straight to CVS or amnio, or skip the screening altogether.
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommends that women of all ages be offered genetic testing and diagnostic testing. Your doctor or genetic counselor should discuss the pros and cons of the available options with you. But ultimately, to test or not to test is a personal decision.

Some women who choose invasive testing are clear in advance that they will terminate the pregnancy if a serious problem is found. Some believe that knowing their child’s special needs helps them prepare emotionally for future challenges. In certain cases, they may need to transfer to a better equipped specialist hospital.
What Is Amniocentesis?
There is no right decision. Each parent will have different feelings about acceptable risks and may reach different conclusions in similar situations.
Before making a decision, you should discuss all of these issues with your partner, your health care provider, and possibly a genetic counselor.
1. An ultrasound is used to measure your baby and check his basic anatomy. (Some testing centers do this when you have your amniocentesis. Others do it beforehand.)
2. You lie on the examination table and your abdomen is cleaned with alcohol or iodine solution to reduce the risk of infection.
What Is Amniocentesis?
3. Ultrasound locates the amniotic sac at a safe distance from the baby and the placenta.
5. The doctor removes a small amount of amniotic fluid—about an ounce or two tablespoons—and withdraws the needle. It may take a few minutes to remove the liquid, but it usually takes less than 30 seconds. Your baby will make more fluid instead of what is taken.
You may feel stressed, stressed, or overwhelmed during the process—or you may feel completely uncomfortable. The amount of discomfort or pain varies between women and from pregnancy to pregnancy. You can numb your abdomen first with a local anesthetic if you want, but the pain from the injection can be worse than the pain from the amniotic fluid itself, and most mothers will decide that one injection is enough.
Antepartum Testing And Monitoring
Note: If your blood is Rh negative, you will need an Rh immunoglobulin shot after the amniocentesis, unless the baby’s father is Rh negative. (Your baby’s blood may mix with yours during the procedure and may not be compatible.)
You will need to rest all day, so book someone to drive you home.
Some of the initial test results may be available in a few days. For example, in some cases, a technique called fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) can be used to diagnose selected disorders. These results are available quickly.
However, some tests may take several weeks. The lab also takes some of the baby’s live cells from the liquid and lets them multiply for a week or two, then checks the cells for chromosomal abnormalities and certain birth defects. (You can find out the gender of your baby if you want.)
Older Mothers And Increased Impact Of Prenatal Screening: Stable Livebirth Prevalence Of Trisomy 21 In The Netherlands For The Period 2000–2013
You will be offered genetic counseling and a consultation with a maternal-fetal specialist to get more information and discuss your options. Some women choose to terminate the pregnancy, while others choose to continue.
Whichever method you choose, you may find that you need additional advice or support. Some women find support groups helpful, some may need individual counseling, and some may choose both. Make sure you tell your doctor and genetic counselor if you need more help so they can give you the right referral.
The editorial team is committed to providing the most useful and reliable information in the world about pregnancy and parenthood. When we create and update content, we rely on reliable sources: reputable health organizations, professional groups of doctors and other professionals, and studies published in peer-reviewed journals. We believe you should always know the source of the information you see. Read more in our editorial and clinical reviews.

Karen Miles is an author and pregnancy and parenting expert who has been making an impact for over 20 years. He wants to provide parents with timely and useful information so they can make the right decisions for their families. Her favorite gig is “Mama Karen” to her four grown children and “Nana” to her nine grandchildren.
Guide To Understanding Prenatal Screening Tests |
2weeks pregnant3weeks pregnant4weeks pregnant5weeks pregnant6weeks pregnant7weeks pregnant8weeks pregnant9weeks pregnant10weeks pregnant11weeks pregnant12weeks pregnant13weeks pregnant14weeks pregnant15weeks pregnant16weeks pregnant17weeks pregnant18weeks pregnant19weeks pregnant20weeks pregnant21weeks pregnant22weeks pregnant23weeks pregnant24weeks pregnant25weeks pregnant26weeks pregnant27weeks pregnant28weeks pregnant29weeks pregnant30weeks pregnant31weeks pregnant32weeks pregnant33weeks pregnant34weeks pregnant35weeks pregnant36weeks pregnant37weeks pregnant38weeks pregnant39weeks pregnant40weeks pregnant41weeks pregnantAmniocentesis is a procedure used to take out a small amniotic fluid sample for testing. This is the fluid that surrounds the fetus in a pregnant woman. Amniotic fluid is a clear, pale yellow fluid that:
Amniotic fluid contains cells provided by the fetus, as well as various enzymes, proteins, hormones and other substances. These cells carry genetic information that can be used to diagnose genetic disorders and diagnose neural tube defects (ONTDs), such as spina bifida. Testing can also be done to look for genetic defects and metabolic disorders based on family history.
Amniotic fluid also contains other substances that provide information about the unborn baby. This process can be done at the end of pregnancy to check